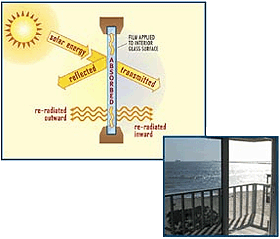
How Window Film Affects Glass
Glass is designed to be a barrier from exterior elements (i.e. wind, rain and snow) while providing a natural view of the outside world. When solar energy – comprised of heat, light and UV Rays – hits a glass window almost 90% of the energy is transmitted through.
When window film is applied to glass, its properties including special dyes and/or metals incorporated within the film act as a solar energy barrier either by absorbing part of the energy or reflecting a portion of the energy away from the glass.
The level of absorption and reflectance is dependant on how the film is constructed. Dyed films contain no metal and are considered non-reflective because they only absorb solar energy. They are not as effective in controlling solar heat and light because they do not provide any solar reflectance. On the other hand, metallized films provide both solar absorption and reflectance. They do a much better job of solar control since the metal properties within the film reflect both heat and light away from the glass surface.